Rotator Cuff Injury
What is a rotator cuff injury?
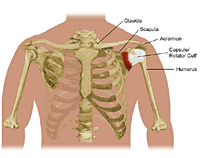
Your rotator cuff consists of muscles and tendons that hold your shoulder in place. It is one of the most important parts of your shoulder.
Your rotator cuff allows you to lift your arms and reach upward. Each year, millions of people in the United States go to their healthcare providers because of a rotator cuff problem. A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults.
What are the symptoms of a rotator cuff tear?
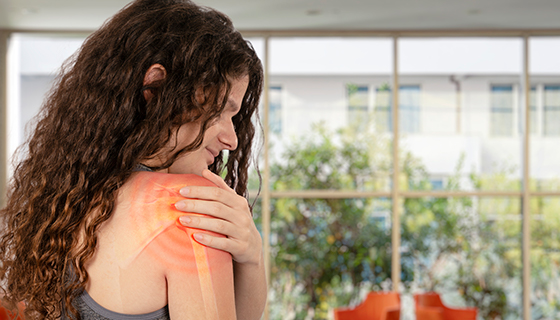
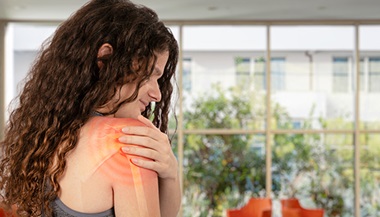
The following are the most common symptoms of a rotator cuff tear. However, you may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
-
Recurrent pain, especially with certain activities
-
Pain that prevents you from sleeping on your injured side
-
Grating or cracking sounds when moving your arm
-
Limited ability to move your arm
-
Muscle weakness
The symptoms of a rotator cuff tear may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is a rotator cuff injury diagnosed?
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, diagnostic procedures for a rotator cuff injury may include the following:
-
X-ray. A diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body.
A rotator cuff may tear partially or fully. Partial-thickness tears do not completely sever the tendon from the shoulder.
What causes a rotator cuff injury?
There are 2 main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and degeneration. An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand. It may also develop over time due to repetitive activities. Rotator cuff tears may also happen due to aging, with degeneration of the tissues.
How is a rotator cuff injury treated?
Treatment may include:
-
Rest
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines
-
Strengthening and stretching exercises
-
Ultrasound therapy
-
Corticosteroid injection
-
Surgery (for severe injuries)
Johns Hopkins Shoulder and Elbow Surgery
Our team of orthopaedic shoulder and elbow specialists diagnoses and treats common and complex shoulder and elbow conditions, including rotator cuff tears, ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) tears, and shoulder and elbow arthritis. Our specialists are also skilled in different shoulder replacement approaches.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Notify your healthcare provider if:
-
Your pain becomes worse or begins to interfere with your normal activities or ability to sleep well
-
You can’t use your shoulder as much as you were able to previously
Key points about rotator cuff injury
-
Your rotator cuff allows you to lift your arms and reach upward.
-
There are 2 main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and degeneration.
-
The symptoms of a rotator cuff tear may resemble other conditions or medical problems. It is important to talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
-
Your healthcare provider will determine specific treatment for your rotator cuff injury.